Locus 14
Top associations per target
| Target | cis/trans | Study | SNP | SNP location | Maj/min allele | MAF | N | βinv | seinv | Pinv | fclog | Plog | Praw |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ARTS1 | cis | Discovery | rs17482078 | 5:96,118,866 | C/T | 0.19 | 993 | -1.142 | 0.044 | 3×10-115 | -1.710 | 9.8×10-157 | 2.2×10-112 |
| ARTS1 | cis | Replication | rs17482078 | 5:96,118,866 | G/A | 0.09 | 337 | -0.901 | 0.117 | 1.7×10-13 | -1.550 | 1.4×10-12 | 1.6×10-12 |
Regional association plots
Endoplasmic reticulum aminopeptidase 1 (ARTS1)
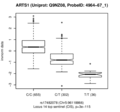
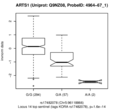
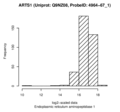
Boxplots and histograms for top associations
Endoplasmic reticulum aminopeptidase 1 (ARTS1)
| Target (abbrv.) | ARTS1 |
| Target (full name) | Endoplasmic reticulum aminopeptidase 1 |
| Somalogic ID (Sequence ID) | SL007729 (4964-67_1) |
| Entrez Gene Symbol | ERAP1 |
| UniProt ID | Q9NZ08 |
| UniProt Comment |
|
| Reactome |
|
All locus annotations are based on the sentinel SNP (rs17482078) and 22 proxy variant(s) that is/are in linkage disequilibrium r2 ≥ 0.8. Linkage disequilibrium is based on data from the 1000 Genomes Project, phase 3 version 5, European population and was retrieved using SNiPA's Block Annotation feature.
Download the detailed results of SNiPA's block annotation (PDF)
Linked genes
| Genes hit or close-by |
|
| Potentially regulated genes |
|
| eQTL genes |
|
Results from other genome-wide association studies
| Trait | P | Study | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gene expression of ERAP1 [probe 214012_at] in lymphoblastoid cell lines | 1.4×10-22 | 17873877 (PMID) | GRASP2 eQTL |
| Gene expression of ERAP1 [probe 209788_s_at] in lymphoblastoid cell lines | 9.4×10-17 | 17873877 (PMID) | GRASP2 eQTL |
| Gene expression of ARTS-1 in CD4+ lymphocytes | 5.8×10-14 | 20833654 (PMID) | GRASP2 eQTL |
| Ankylosing spondylitis (HLA-B27 positive) | 1.5×10-10 | 21743469 (PMID) | GRASP2 nonQTL |
| Gene expression of ERAP1 [probeset 214012_at] in sputum | 1.7×10-10 | 21949713 (PMID) | GRASP2 eQTL |
| Gene expression of ERAP1 (probeID ILMN_2336220) in temporal cortex in Alzheimer's disease cases and controls | 2.7×10-9 | 22685416 (PMID) | GRASP2 eQTL |
| Differential exon level expression of ERAP1 [probe 2868133] in peripheral blood mononuclear cells | 3.5×10-9 | 19222302 (PMID) | GRASP2 eQTL |
| Gene expression of ERAP1 in peripheral blood monocytes | 5.6×10-9 | 20502693 (PMID) | GRASP2 eQTL |
| Differential splicing of ARTS-1 [probeset 2868133] in lymphoblastoid cell lines | 1×10-8 | 19052777 (PMID) | GRASP2 eQTL |
| Ankylosing spondylitis | 1.1×10-8 | 21743469 (PMID) | GRASP2 nonQTL |
| Behcet's disease | 4×10-8 | 23291587 (PMID) | GWAS Catalog via SNiPA |
| Gene expression of ERAP1 in T cells | 9.2×10-8 | 19644074 (PMID) | GRASP2 eQTL |
| Differential exon level expression of ERAP1 [probe 2868144] in peripheral blood mononuclear cells | 2.2×10-7 | 19222302 (PMID) | GRASP2 eQTL |
| Differential exon level expression of ERAP1 [probe 2868145] in peripheral blood mononuclear cells | 2.6×10-7 | 19222302 (PMID) | GRASP2 eQTL |
| Gene expression of ERAP1 (probeID ILMN_2336220) in cerebellum in Alzheimer's disease cases and controls | 6.3×10-7 | 22685416 (PMID) | GRASP2 eQTL |
| Gene expression of ERAP1 in Lymphoblastoid cell lines | 6.5×10-7 | 19644074 (PMID) | GRASP2 eQTL |
| Differential exon level expression of ERAP1 [probe 2868142] in peripheral blood mononuclear cells | 7.9×10-7 | 19222302 (PMID) | GRASP2 eQTL |
| Gene expression of KCNH8 in peripheral blood monocytes | 7.7×10-6 | 20502693 (PMID) | GRASP2 eQTL |
| Differential exon level expression of ERAP1 [probe 2868161] in peripheral blood mononuclear cells | 8×10-6 | 19222302 (PMID) | GRASP2 eQTL |
| Gene expression of ERAP1 [probeset 210385_s_at] in sputum | 1.4×10-4 | 21949713 (PMID) | GRASP2 eQTL |
| Gene expression of LRAP in blood | 4×10-4 | 21829388 (PMID) | GRASP2 eQTL |
Two independent pQTLs, confirmed by strong eQTLs, with additive effect, co-association to ankylosing spondylitis suggests additive risk.
Two strong cis-associations endoplasmic reticulum aminopeptidase 1 (ERAP1, aka ARTS1). SNP rs26496 (Locus 11) is associated with ankylosing spondylitis [PubMed]. SNP rs17482078 (Locus 14, r2=0.059 with rs26496) is associated with Behcet's disease. Hong et al. [PubMed] report an mQTL with SNP rs27529 (r2=0.46 with rs26496) with a metabolite of unknown identity (MS peaks 616.7 m/z, 666.3 m/z, 489.2 m/z). Imputed data reveals at least two independent hits with p<10-120. Interaction between ERAP1 and HLA-B27 was reported by Evans et al. [PubMed] . That paper also provides experimental evidence that rs30187 (r2=0.46 with rs26496) and rs17482078 have ~40% slower rates of substrate trimming than wild-type ERAP1, but results are based only on a small set of experiments (N=3). See Locus 251 for a non-replicated associations with IL23R in relation to ankylosing spondylitis. Evans et al. [PubMed] discuss the interaction of ERAP1 and IL23R.
The information gathered here is a result of an attempt to keep track of all interesting information that we encountered while investigating these loci. Please bear in mind that the annotation given here is neither complete nor free of errors, and that all information provided here should be confirmed by additional literature research before being used as a basis for firm conclusions or further experiments.