Locus annotations
Locus 235
Top associations per target
| Target | cis/trans | Study | SNP | SNP location | Maj/min allele | MAF | N | βinv | seinv | Pinv | fclog | Plog | Praw |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C4 | cis | Discovery | rs8283 | 6:32,083,300 | A/G | 0.19 | 994 | 0.487 | 0.056 | 2.3×10-17 | 1.090 | 7.7×10-15 | 1×10-16 |
| C4 | cis | Replication | rs8283 | 6:32,083,300 | A/G | 0.39 | 337 | 0.571 | 0.070 | 7.5×10-15 | 1.150 | 6.9×10-12 | 1.9×10-14 |
Regional association plots
Complement C4 (C4)
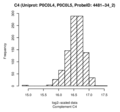
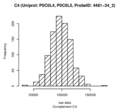
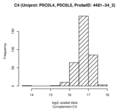
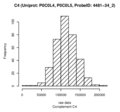
Boxplots and histograms for top associations
Complement C4 (C4)
| Target (abbrv.) | C4 |
| Target (full name) | Complement C4 |
| Somalogic ID (Sequence ID) | SL000316 (4481-34_2) |
| Entrez Gene Symbol | C4A, C4B |
| UniProt ID | P0C0L4, P0C0L5 |
| UniProt Comment |
|
| Wiki Pathways |
|
| Reactome |
|
All locus annotations are based on the sentinel SNP (rs8283).
Download the detailed results of SNiPA's block annotation (PDF)
Linked genes
| Genes hit or close-by | |
| eQTL genes |
|
Results from other genome-wide association studies
| Trait | P | Study | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rheumatoid arthritis | 3.8×10-51 | 20453842 (PMID) | GRASP2 nonQTL |
| HIV-1 control | 2.2×10-9 | 21051598 (PMID) | GRASP2 nonQTL |
| Crohn's disease | 1×10-6 | Supplemental file |