Locus annotations
Locus 287
Top associations per target
| Target | cis/trans | Study | SNP | SNP location | Maj/min allele | MAF | N | βinv | seinv | Pinv | fclog | Plog | Praw |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| sLeptin R | cis | Discovery | rs4655537 | 1:66,058,801 | G/A | 0.35 | 994 | 0.350 | 0.044 | 7.4×10-15 | 1.240 | 5.8×10-16 | 6.4×10-16 |
| sLeptin R | cis | Replication | rs4655537 | 1:66,058,801 | G/A | 0.37 | 337 | 0.389 | 0.066 | 1×10-8 | 1.250 | 2.1×10-10 | 1.6×10-8 |
Regional association plots
Leptin receptor (sLeptin R)
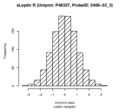
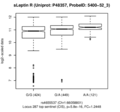
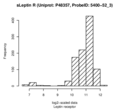
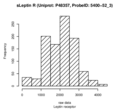
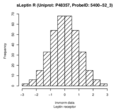
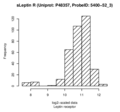
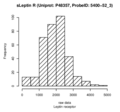
Boxplots and histograms for top associations
Leptin receptor (sLeptin R)
| Target (abbrv.) | sLeptin R |
| Target (full name) | Leptin receptor |
| Somalogic ID (Sequence ID) | SL003184 (5400-52_3) |
| Entrez Gene Symbol | LEPR |
| UniProt ID | P48357 |
| UniProt Comment |
|
| Targeted by drugs (based on IPA annotation) |
|
| Biomarker applications (based on IPA annotation) |
|
| Wiki Pathways |
|
| Pathway Interaction Database |
|
| Reactome |
|
All locus annotations are based on the sentinel SNP (rs4655537) and 1 proxy variant(s) that is/are in linkage disequilibrium r2 ≥ 0.8. Linkage disequilibrium is based on data from the 1000 Genomes Project, phase 3 version 5, European population and was retrieved using SNiPA's Block Annotation feature.
Download the detailed results of SNiPA's block annotation (PDF)
Linked genes
| Genes hit or close-by |
|
Results from other genome-wide association studies
| Trait | P | Study | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Plasma soluble leptin receptor (sOB-R) levels | 2.8×10-12 | 20167575 (PMID) | GRASP2 nonQTL |
| C-reactive protein (CRP) | 6.6×10-10 | 23505291 (PMID) | GRASP2 nonQTL |
| Plasma C-reactive protein (female) | 3.3×10-9 | 18439548 (PMID) | GRASP2 nonQTL |
| Baseline acute-phase serum amyloid concentrations | 1.6×10-8 | 21124955 (PMID) | GRASP2 nonQTL |
| cg00046625 (chr1:66258784) | 1.1×10-6 | 10.1101/033084 (DOI) | BIOS QTL cis-meQTLs |