Locus 348
Top associations per target
| Target | cis/trans | Study | SNP | SNP location | Maj/min allele | MAF | N | βinv | seinv | Pinv | fclog | Plog | Praw |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Trypsin 2 | trans | Discovery | rs3134906 | 7:142,505,154 | G/A | 0.50 | 995 | 0.308 | 0.042 | 4.2×10-13 | 1.130 | 5.4×10-13 | 4.2×10-11 |
| Trypsin 2 | trans | Replication | rs3134906 | 7:142,505,154 | G/A | 0.38 | 337 | 0.147 | 0.077 | 0.058 | 1.080 | 0.059 | 0.156 |
Regional association plots
Trypsin-2 (Trypsin 2)
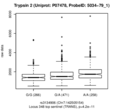
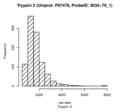
Boxplots and histograms for top associations
Trypsin-2 (Trypsin 2)
| Target (abbrv.) | Trypsin 2 |
| Target (full name) | Trypsin-2 |
| Somalogic ID (Sequence ID) | SL010388 (5034-79_1) |
| Entrez Gene Symbol | PRSS2 |
| UniProt ID | P07478 |
| UniProt Comment |
|
| Reactome |
|
All locus annotations are based on the sentinel SNP (rs3134906) and 7 proxy variant(s) that is/are in linkage disequilibrium r2 ≥ 0.8. Linkage disequilibrium is based on data from the 1000 Genomes Project, phase 3 version 5, European population and was retrieved using SNiPA's Block Annotation feature.
Download the detailed results of SNiPA's block annotation (PDF)
Linked genes
| Genes hit or close-by |
|
| Potentially regulated genes |
|
| eQTL genes |
Results from other genome-wide association studies
| Trait | P | Study | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gene expression of [probe 6280750 centered at chr7:142207470] in blood | 4.6×10-21 | 21829388 (PMID) | GRASP2 eQTL |
| Gene expression of ENST00000390401 in blood | 1.4×10-9 | 21829388 (PMID) | GRASP2 eQTL |
| Gene expression of EPHB6 in peripheral blood monocytes | 6.4×10-9 | 20502693 (PMID) | GRASP2 eQTL |
| Gene expression of ENST00000390418///ENST00000390419 in blood | 1.8×10-6 | 21829388 (PMID) | GRASP2 eQTL |
| Gene expression of C7orf34///KEL in blood | 1.7×10-4 | 21829388 (PMID) | GRASP2 eQTL |
| Gene expression of ENST00000390392 in blood | 3.2×10-4 | 21829388 (PMID) | GRASP2 eQTL |
Functional match between the T cell receptor beta locus and T-cell receptor beta variable and joining genes.
Non-replicated trans-association with Trypsin-2 (PRSS2). Cis-SNP is in T-cell receptor beta variable and joining repertoire. PRSS2 is localized to the T cell receptor beta locus on chromosome 7. Functional match between the T cell receptor beta locus and T-cell receptor beta variable and joining genes.
The information gathered here is a result of an attempt to keep track of all interesting information that we encountered while investigating these loci. Please bear in mind that the annotation given here is neither complete nor free of errors, and that all information provided here should be confirmed by additional literature research before being used as a basis for firm conclusions or further experiments.