Locus 43
Top associations per target
| Target | cis/trans | Study | SNP | SNP location | Maj/min allele | MAF | N | βinv | seinv | Pinv | fclog | Plog | Praw |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
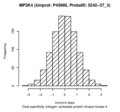
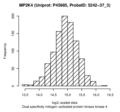
| MP2K4 | trans | Discovery | rs1042445 | 3:186,395,436 | C/T | 0.23 | 997 | -0.879 | 0.043 | 8.4×10-78 | -1.300 | 1.3×10-80 | 6×10-67 |
| MP2K4 | trans | Replication | rs1042445 | 3:186,395,436 | G/A | 0.26 | 337 | -0.726 | 0.069 | 1.2×10-22 | -1.340 | 2.6×10-23 | 3.4×10-22 |
| CD27 | trans | Discovery | rs1042445 | 3:186,395,436 | C/T | 0.23 | 997 | -0.556 | 0.049 | 1.6×10-28 | -1.090 | 2.3×10-17 | 9.2×10-10 |
| CD27 | trans | Replication | rs1042445 | 3:186,395,436 | G/A | 0.26 | 337 | -0.234 | 0.082 | 0.005 | -1.070 | 0.027 | 0.061 |
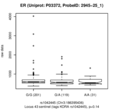
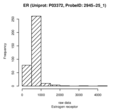
| ER | trans | Discovery | rs1042445 | 3:186,395,436 | C/T | 0.23 | 997 | -0.438 | 0.050 | 6.2×10-18 | -1.060 | 2.4×10-6 | 0.068 |
| ER | trans | Replication | rs1042445 | 3:186,395,436 | G/A | 0.26 | 337 | -0.241 | 0.071 | 0.001 | -1.060 | 0.015 | 0.103 |
Regional association plots
Dual specificity mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 4 (MP2K4)
CD27 antigen (CD27)
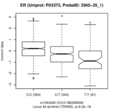
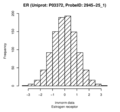
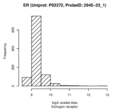
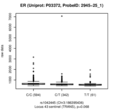
Estrogen receptor (ER)
Boxplots and histograms for top associations
Dual specificity mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 4 (MP2K4)
| inverse-normalized probe levels | log2 transformed probe levels | raw probe levels | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Discovery study |

|

|
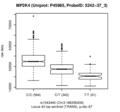
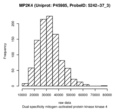
|
| Replication study |


|

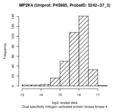
|

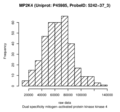
|
CD27 antigen (CD27)
| inverse-normalized probe levels | log2 transformed probe levels | raw probe levels | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Discovery study |


|

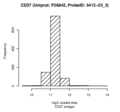
|
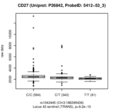
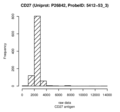
|
| Replication study |


|


|


|
Estrogen receptor (ER)
Dual specificity mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 4 (MP2K4)
| Target (abbrv.) | MP2K4 |
| Target (full name) | Dual specificity mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 4 |
| Somalogic ID (Sequence ID) | SL007237 (5242-37_3) |
| Entrez Gene Symbol | MAP2K4 |
| UniProt ID | P45985 |
| UniProt Comment |
|
| Wiki Pathways |
|
| Pathway Interaction Database |
|
| Reactome |
|
| Pathway Studio |
|
CD27 antigen (CD27)
| Target (abbrv.) | CD27 |
| Target (full name) | CD27 antigen |
| Somalogic ID (Sequence ID) | SL004134 (5412-53_3) |
| Entrez Gene Symbol | CD27 |
| UniProt ID | P26842 |
| UniProt Comment |
|
| Biomarker applications (based on IPA annotation) |
|
Estrogen receptor (ER)
| Target (abbrv.) | ER |
| Target (full name) | Estrogen receptor |
| Somalogic ID (Sequence ID) | SL000007 (2945-25_1) |
| Entrez Gene Symbol | ESR1 |
| UniProt ID | P03372 |
| UniProt Comment |
|
| Targeted by drugs (based on IPA annotation) |
|
| Biomarker applications (based on IPA annotation) |
|
| Wiki Pathways |
|
| Pathway Interaction Database |
|
| Reactome |
|
All locus annotations are based on the sentinel SNP (rs1042445) and 4 proxy variant(s) that is/are in linkage disequilibrium r2 ≥ 0.8. Linkage disequilibrium is based on data from the 1000 Genomes Project, phase 3 version 5, European population and was retrieved using SNiPA's Block Annotation feature.
Download the detailed results of SNiPA's block annotation (PDF)
Linked genes
| Genes hit or close-by |
|
Results from other genome-wide association studies
| Trait | P | Study | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Activated partial thromboplastin time | 6.6×10-53 | 22703881 (PMID) | GRASP2 nonQTL |
HRG may have a regulatory role on MAP2K4, possibly also on CD27 and ESR1.
Locus 31 harbours a replicated trans-association with Dual specificity mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 4 (MAP2K4) and a replicated cis-association with Histidine-rich glycoprotein (HRG). Elevated levels of HRG are associated with thrombophilia (OMIM #613116). Locus 43 harbours a second replicated trans-association with MAP2K4 in the same genetic region. The associated SNP rs1042445 is a coding variant in HRG. In addition, there are two non-replicated, but in QMDiab still nominally significant trans-pQTL with CD27 antigen (CD27, p=4.7×10-3 in QMDiab) and Estrogen receptor (ESR1, p=8.3×10-4 in QMDiab).
The information gathered here is a result of an attempt to keep track of all interesting information that we encountered while investigating these loci. Please bear in mind that the annotation given here is neither complete nor free of errors, and that all information provided here should be confirmed by additional literature research before being used as a basis for firm conclusions or further experiments.