Locus 54
Top associations per target
| Target | cis/trans | Study | SNP | SNP location | Maj/min allele | MAF | N | βinv | seinv | Pinv | fclog | Plog | Praw |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| G-CSF | trans | Discovery | rs5167 | 19:45,448,465 | T/G | 0.35 | 997 | 0.750 | 0.039 | 2.1×10-69 | 1.200 | 1.2×10-28 | 0.117 |
| G-CSF | trans | Replication | rs5167 | 19:45,448,465 | A/C | 0.36 | 337 | 0.334 | 0.074 | 9.5×10-6 | 1.050 | 0.165 | 0.273 |
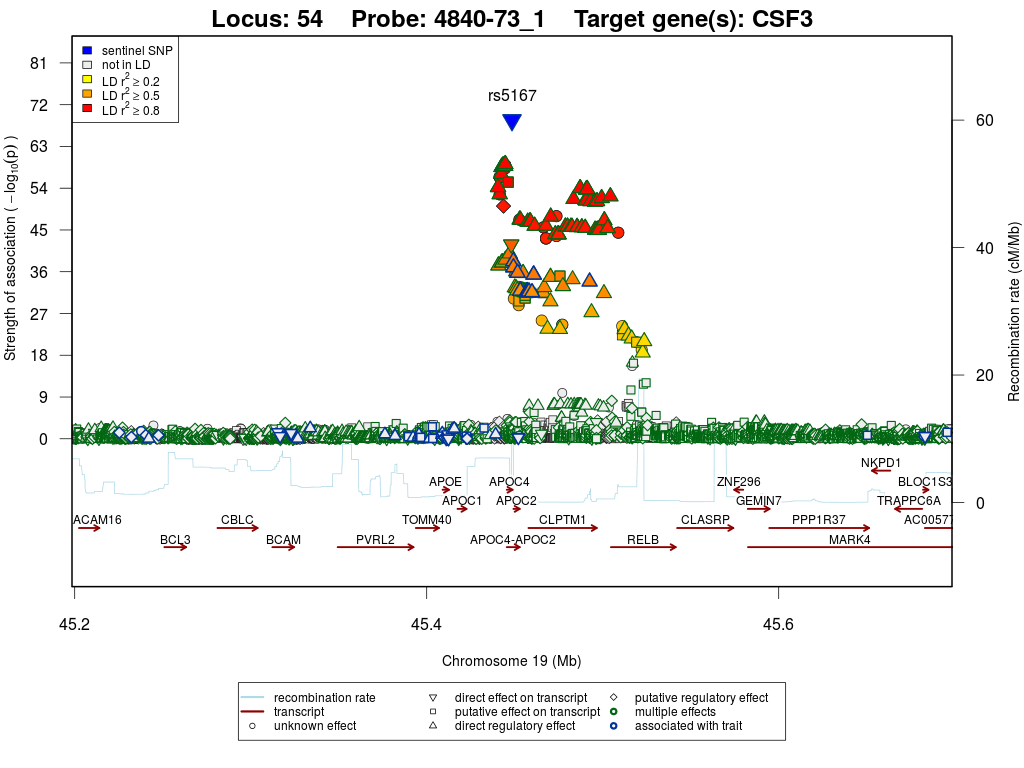
Regional association plots
Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF)
Boxplots and histograms for top associations
Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF)
| Target (abbrv.) | G-CSF |
| Target (full name) | Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor |
| Somalogic ID (Sequence ID) | SL001729 (4840-73_1) |
| Entrez Gene Symbol | CSF3 |
| UniProt ID | P09919 |
| UniProt Comment |
|
| Targeted by drugs (based on IPA annotation) |
|
| Biomarker applications (based on IPA annotation) |
|
| Wiki Pathways |
|
| Pathway Studio |
|
All locus annotations are based on the sentinel SNP (rs5167) and 11 proxy variant(s) that is/are in linkage disequilibrium r2 ≥ 0.8. Linkage disequilibrium is based on data from the 1000 Genomes Project, phase 3 version 5, European population and was retrieved using SNiPA's Block Annotation feature.
Download the detailed results of SNiPA's block annotation (PDF)
Linked genes
| Genes hit or close-by |
|
| Potentially regulated genes | |
| eQTL genes |
Results from other genome-wide association studies
| Trait | P | Study | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| cg06736138 (chr19:45444836) | 5.5×10-83 | 10.1101/033084 (DOI) | BIOS QTL cis-meQTLs |
| Alzheimer's disease | 2.5×10-18 | 24162737 (PMID) | Supplemental file |
| HDL cholesterol | 4.9×10-16 | 24097068 (PMID) | Supplemental file |
| Late onset Alzheimer's disease | 3.4×10-8 | 21460841 (PMID) | GRASP2 nonQTL |
| Triglycerides | 2.2×10-6 | 24097068 (PMID) | Supplemental file |
| Differential exon level expression of CLPTM1 [probe 3835952] in brain cortex | 6.1×10-6 | 19222302 (PMID) | GRASP2 eQTL |
| Height | 2×10-5 | 25282103 (PMID) | Supplemental file |
| Total cholesterol | 3.9×10-5 | 20686565 (PMID) | GRASP2 nonQTL |
| Gene expression of BLOC1S3 [probe ILMN_4337] in osteoblasts treated with pge-2 | 1.3×10-4 | 21283786 (PMID) | GRASP2 eQTL |
| Schizophrenia | 2×10-4 | 23974872 (PMID) | Supplemental file |
| Bipolar disorder vs. Schizophrenia | 2.9×10-4 | 24280982 (PMID) | Supplemental file |
| Hip circumfence, adjusted for BMI | 4.7×10-4 | 25673412 (PMID) | Supplemental file |
APOC4 and CSF3 may interact.
This locus is located in the APOE/C1/C4/C2 cluster and harbours a replicated trans-association with Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (CSF3). rs5167 is linked to rs35336243 (r2>0.8), which associates with Alzheimer's disease (p=2.55×10-18) in the International Genomics of Alzheimer's Project (IGAP) stage 1 data. From the data at hand it is however not possible to say whether this is an independent association signal with AD, or a spill-over from the main AD variant in APOE. This variant is an amino acid changing variant in APOC4 (L96R). Since rs5167 also shows the strongest association with CSF3 when using imputed SNPs, it is likely that this variant in APOC4 causes differential protein expression of CSF3.
The information gathered here is a result of an attempt to keep track of all interesting information that we encountered while investigating these loci. Please bear in mind that the annotation given here is neither complete nor free of errors, and that all information provided here should be confirmed by additional literature research before being used as a basis for firm conclusions or further experiments.