Locus 7
Top associations per target
| Target | cis/trans | Study | SNP | SNP location | Maj/min allele | MAF | N | βinv | seinv | Pinv | fclog | Plog | Praw |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Siglec-3 | cis | Discovery | rs12459419 | 19:51,728,477 | C/T | 0.28 | 995 | -1.133 | 0.034 | 2.9×10-165 | -1.610 | 1.4×10-185 | 2.7×10-167 |
| Siglec-3 | cis | Replication | rs3865444 | 19:51,727,962 | C/A | 0.17 | 337 | -1.028 | 0.056 | 2×10-52 | -1.590 | 1.5×10-59 | 4.2×10-41 |
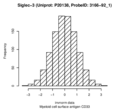
Regional association plots
Myeloid cell surface antigen CD33 (Siglec-3)
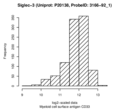
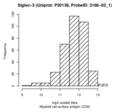
Boxplots and histograms for top associations
Myeloid cell surface antigen CD33 (Siglec-3)
| Target (abbrv.) | Siglec-3 |
| Target (full name) | Myeloid cell surface antigen CD33 |
| Somalogic ID (Sequence ID) | SL005215 (3166-92_1) |
| Entrez Gene Symbol | CD33 |
| UniProt ID | P20138 |
| UniProt Comment |
|
| Targeted by drugs (based on IPA annotation) |
|
| Biomarker applications (based on IPA annotation) |
|
All locus annotations are based on the sentinel SNP (rs12459419) and 5 proxy variant(s) that is/are in linkage disequilibrium r2 ≥ 0.8. Linkage disequilibrium is based on data from the 1000 Genomes Project, phase 3 version 5, European population and was retrieved using SNiPA's Block Annotation feature.
Download the detailed results of SNiPA's block annotation (PDF)
Linked genes
| Genes hit or close-by |
|
| Potentially regulated genes |
|
| eQTL genes |
Results from other genome-wide association studies
| Trait | P | Study | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alzheimer's disease | 1.6×10-9 | 21460840 (PMID) | GRASP2 nonQTL |
| Late onset Alzheimer's disease | 1.6×10-9 | 21460841 (PMID) | GRASP2 nonQTL |
| Alzheimer's disease (late onset) | 2×10-9 | 21460841 (PMID) | GWAS Catalog via SNiPA |
| P20138 protein abundance levels | 5.1×10-9 | 22595970 (PMID) | GRASP2 pQTL |
Changes in CD33 protein levels co-associate with AD.
This locus harbours a replicated cis-pQTL with Myeloid cell surface antigen CD33 (CD33, aka Siglec-3). This SNP is an A14V amino acid exchange and in near-perfect LD with rs3865444. rs3865444 is an Alzheimer's disease risk variant [PubMed]. Increased expression of CD33 mRNA was associated with increasing AD pathology in temporal cortex brain samples [PubMed]. Here we show that also protein levels of CD33 associate with rs3865444. See the role of inflammation in Alzheimer's disease in Heppner et al. [PubMed]. See also Hernández-Caselles et al. [PubMed] for alternative splicing in CD33. See Chouraki and Seshadri [PubMed] for the genetics of Alzheimer's.
The information gathered here is a result of an attempt to keep track of all interesting information that we encountered while investigating these loci. Please bear in mind that the annotation given here is neither complete nor free of errors, and that all information provided here should be confirmed by additional literature research before being used as a basis for firm conclusions or further experiments.